Constructing Charge-Delocalized Polycationic Protective Layer by Chitosan for Zinc-Ion Batteries
Citation
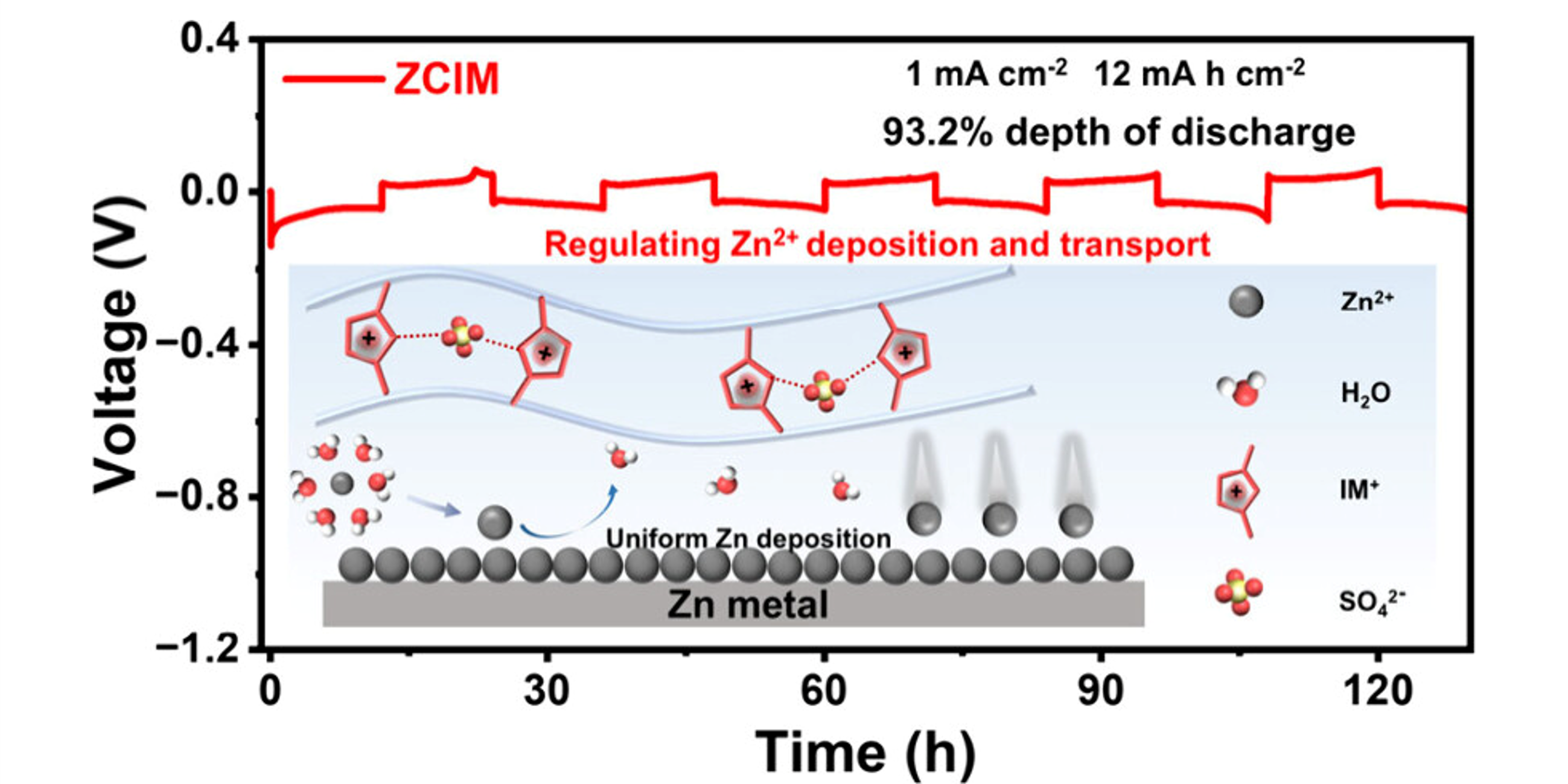
Binbin Ren, Yifan Pan, Yanchun Xie, Yucong Jiao*, and Peiyi Wu*. Constructing Charge-Delocalized Polycationic Protective Layer by Chitosan for Zinc-Ion Batteries. ACS Materials Lett. 2025, 7, 3394-3402.
Abstract
Engineering a polymer-based protective layer on a Zn metal surface can alleviate the side reactions for high Zn reversibility, yet the chain entanglement of the polymer may prolong the pathway and hinder the ion transport for poor battery performance. Here, the Debus-Radziszewski reaction was employed to form an imidazolium cation (IM+) structure in chitosan for high-performance protective layers. The protective layer for Zn metal with chitosan connected by IM+ (ZCIM) owns low entanglement characteristics to facilitate the ion transport channel construction, thus significantly promoting rapid Zn2+ migration kinetics. Moreover, the IM+ renders charge delocalization, thereby improving the electric field distribution on the Zn surface to accelerate stable Zn2+ deposition kinetics. Consequently, the symmetrical Zn battery with ZCIM remains stable at a high depth of discharge of 93.2%, and the Zn/I2 battery with ZCIM demonstrates a high-capacity retention rate of over 89% at a low N/P ratio of 2.6.