Water-Soluble Triphenylphosphine-Derived Microgel as the Template Towards in-Situ Nitrogen, Phosphorus...
Citation
Xiongwei Wang, Yong Liu, and Peiyi Wu*. Water-Soluble Triphenylphosphine-Derived Microgel as the Template Towards in-Situ Nitrogen, Phosphorus Co-Doped Mesoporous Graphene Framework for Supercapacitor and Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 417-427.
Abstract
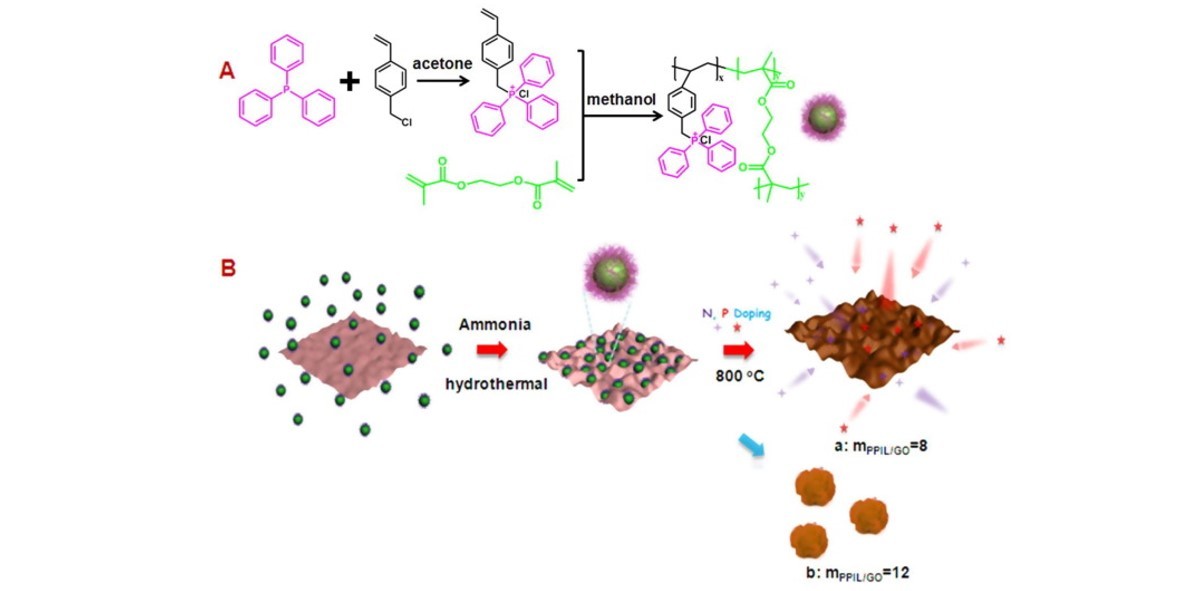
In this work, we endowed the hydrophobic triphenylphosphine (TPP) with vinyl group as a new copolymerization monomer to synthesize water-soluble microgels, in which the hydrophilic and positively charged TPP-derived chain segments are mainly located at the surface. These synthesized microgel is simultaneously used as a soft template and phosphorus dopant to fabricate nitrogen, phosphorus co-doped mesoporous graphene framework (NP-PG) via a facile hydrothermal process containing graphene oxide and ammonia. Self-assembly of graphene oxide sheets and microgels induced by their electrostatic interaction enable a tight contact between them, which would confine the phosphorus doping mostly in the pore walls. The obtained NP-PG, as a metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction, shows a comparable electrocatalytic activity to commercial Pt/C catalyst with a peak potential of −0.18 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) and long-term durability. Additionally, it can also be used as a supercapacitor electrode to achieve a high specific capacitance of 245 F g−1 at 0.5 A g−1 and 95% of capacitance retention even after 3000 cycles at 5 A g−1.